Pharmacokinetics: How Your Body Processes Medications
When you take a pill, it doesn’t just sit there and work. Pharmacokinetics, the study of how the body absorbs, distributes, metabolizes, and excretes drugs. It’s the science behind why some pills work fast, others last all day, and why some can’t be taken with food. This isn’t just for doctors—it affects you every time you swallow a tablet. If your body doesn’t absorb the drug properly, it won’t help. If it breaks it down too quickly, you’ll need more. If it can’t clear it out, you risk side effects.
Drug absorption, how a medicine enters your bloodstream depends on things like stomach acid, whether you ate, or if it’s a capsule vs. liquid. Drug metabolism, how your liver breaks down drugs varies from person to person—age, genetics, even other meds you take can change it. That’s why two people on the same dose can have totally different results. And drug elimination, how your kidneys and liver remove the drug tells you how often you need to take it. Miss a dose? The level drops. Take too much? It builds up. That’s why timing matters.
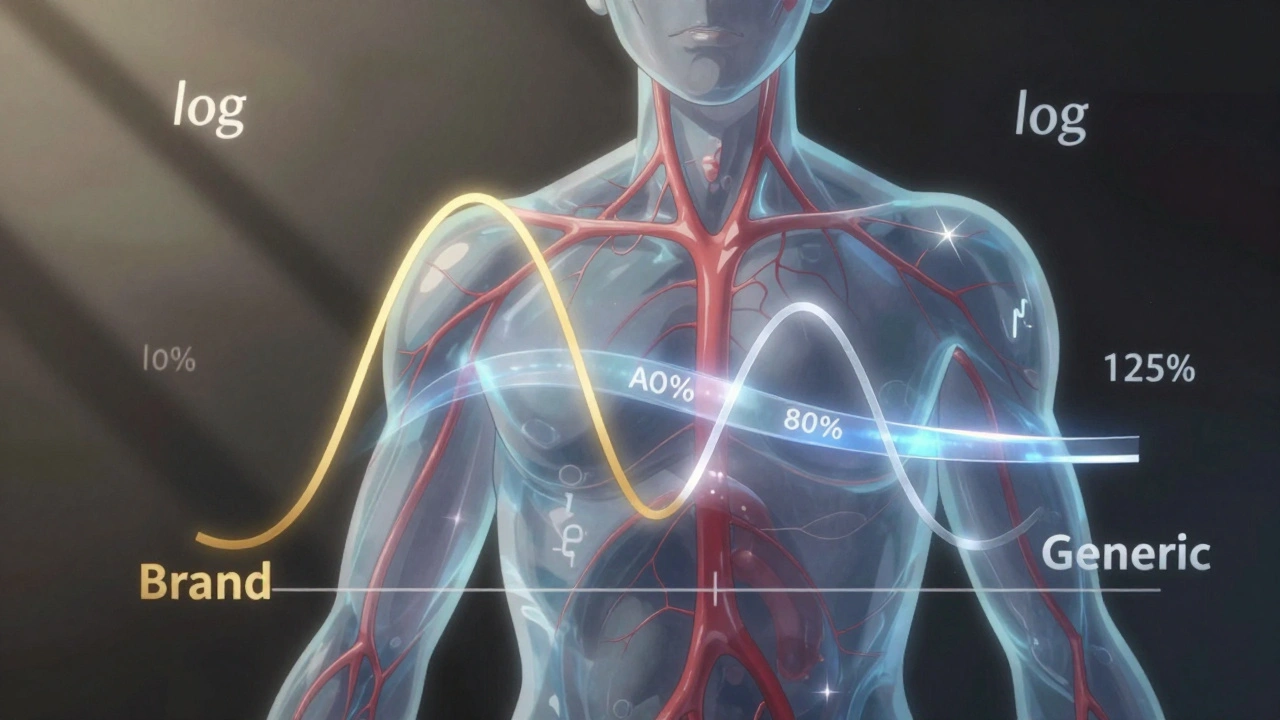
None of this is guesswork. It’s measured in real numbers: bioavailability tells you what percentage of the drug actually reaches your system. A drug with 20% bioavailability means 80% gets lost before it does anything. That’s why some pills are twice the dose of others. It’s also why some generics work differently than brand names—not because they’re weaker, but because of how they’re made, what’s in them, or how fast they dissolve. You’ve seen this in posts about authorized generics, inactive ingredients, and FDA approval processes. All of it ties back to pharmacokinetics.
When you read about why ginseng messes with blood sugar meds, why PPIs block antifungals, or why military troops can’t store pills in hot tents, you’re seeing pharmacokinetics in action. It’s the hidden reason behind drug interactions, dosing schedules, and why your pharmacist asks if you eat grapefruit. This collection of articles doesn’t just list facts—it shows you how the body’s inner mechanics shape real-world outcomes. Whether you’re managing ADHD meds, avoiding fake pills, or picking up generics, understanding pharmacokinetics helps you take control—not just follow instructions.